What Are Semi-Synthetic 7-Hydroxymitragynine Products and Their Implications for Kratom?
Products derived from the botanical Mitragyna speciosa have evolved beyond simple leaf powders into a wide range of offerings, collectively referred to as “kratom.” Traditional whole-leaf products typically maintain consistent concentrations of kratom’s primary alkaloid, mitragynine, and its metabolite, 7-hydroxymitragynine.
Even among extracts, alkaloid levels often adhere to industry norms, with 7-hydroxymitragynine comprising lower than 1–2% of the total content or remaining below the lower limit of quantification. Recently, some manufacturers have introduced novel semi-synthetic products containing 7-hydroxymitragynine in varying forms, such as sublingual tablets, ice cream cones and nasal sprays. These products often deliver 14–25 mg of 7-hydroxymitragynine per labeled dose, with some formulations comprising up to 98% 7-hydroxymitragynine along with other kratom alkaloids.
Fresh kratom leaves contain little to no detectable levels of 7-OH while still attached to the tree. However, once the leaf is harvested and begins to degrade, small traces of 7-OH start to form.
For example, consuming 12 grams of kratom leaf typically provides:
- 120 mg to 150 mg of Mitragynine
- 1.2 mg or less of 7-OH
Alarmingly, certain formulations bypass first-pass metabolism, enhancing bioavailability. Decomposition of mitragynine and formation of 7-OH in liver microsomes was quantified by LC-MS/MS.
Misrepresentation of 7-OH as Kratom Products
The marketing of products containing 7-hydroxymitragynine often creates confusion by equating these semi-synthetic formulations with natural kratom. This branding strategy can mislead kratom-naïve consumers, who may believe these products are as natural, safe, and relatively mild as traditional kratom leaf or plain-leaf powder. You should stick to plain leaf kratom powder if you are a first time consumer, so you can understand how the plant works.
These 7-OH products are significantly more potent than traditional kratom powder and might have their uses in certain contexts. However, they are not purely 100% kratom leaf and should undergo thorough scientific study alongside kratom powder and extracts, so consumers has proper information.
The reality is starkly different between plain leaf kratom powder and 7-hydroxymitragynine products. High-dose, MOR-binding (mu-opioid receptor) formulations of 7-hydroxymitragynine are fundamentally different from natural kratom products. These substances are often produced without adequate human or animal testing, leaving consumers vulnerable to uncharted risks. Acute toxicity is a significant concern, given the potent pharmacological activity of these products.
Furthermore, chronic daily use of such formulations can lead to physical dependence or addiction. The severity of dependence associated with these products is potentially much higher than that observed with traditional kratom leaf-based or even standard extract products. Traditional kratom is typically associated with a light mild physical dependence, manageable with gradual tapering or short breaks in use and similar to coffee. In contrast, these synthetic or semi-synthetic products may involve a more intense and challenging withdrawal process, posing a higher risk for users.
By branding these products as “real kratom,” manufacturers exploit the positive reputation of natural powder while possibly exposing consumers to significantly greater risks. This highlights the need for clear labeling, education, and regulation to protect consumers and ensure they can make informed choices about the products they are using.
What impact does 7-hydroxymitragynine have on data related to Kratom-associated deaths and adverse events?
The reliance on mitragynine as a forensic marker for kratom use further complicates matters. If fatalities are related to 7-hydroxymitragynine it may mistakenly implicate kratom, as mitragynine present in these products often results from incomplete conversion during synthesis. Additionally, current 7-hydroxymitragynine products contain trace mitragynine and unknown chemicals that remain untested for safety. The risks associated with these unidentified substances and high-dose 7-hydroxymitragynine are significant until they are properly studied and deemed safe.
Two of the compound peaks were previously unknown. These compounds have now been identified as 7-Hydroxymitragynine N-oxide and rearranged N-acylpyrazinylindoles. These chemicals have not been documented in scientific literature, are absent from kratom leaves, and have never been consumed by humans. Their formation requires chemical oxidation and rearrangement reactions that are not part of the natural biosynthetic pathways of kratom.
The policy ramifications of these semi-synthetic products remain uncertain. Adverse events or fatalities linked to 7-hydroxymitragynine could jeopardize the regulatory future of kratom, which is used by an estimated 10–15 million U.S. adults.
Policymakers must differentiate between traditional kratom products and high-potency 7-hydroxymitragynine products synthesized in unregulated or makeshift laboratories. Equating the two is akin to conflating synthetic cannabinoids with natural cannabis or hemp.
While organic kratom products have not demonstrated widespread harm to public health and remain federally unscheduled, these novel semi-synthetic products present significant risks. Clinicians must screen patients for their use, and policymakers must establish clear distinctions to safeguard public health and support informed regulatory decisions.
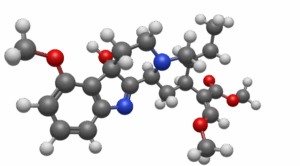
7-OH-Hydroxy Mitragynine – A metabolite of the kratom drying process. It is also coverted in the liver at a rate of 45% after 2 hours.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
- Kirsten E. Smith: Conceptualization; writing—original draft.
- Edward W. Boyer: Conceptualization; writing—original draft.
- Oliver Grundmann: Conceptualization; writing—original draft.
- Christopher R. McCurdy: Conceptualization; writing—original draft.
- Abhisheak Sharma: Conceptualization; writing—original draft.
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
Kirsten E. Smith, K.E.S. has been a paid scientific advisor to the International Plant and Herbal Alliance and The Global Kratom Coalition. K.E.S., O.G., E.W.B. and C.R.M. have served as expert witnesses in legal cases related to kratom.
Conclusion
While 7-HMG is a natural component of the kratom drying process and contributes minimally to its effects, enhancing or isolating it in products significantly increases the risks of dependency, health issues, and regulatory scrutiny. Plain leaf kratom remains the safer option according to a recent FDA study, aligning with traditional practices and supporting a more balanced and sustainable approach to its use.
While plain leaf has a history of safe, balanced use, semi-synthetic derivatives pose challenges that threaten not only individual health but also the public perception and regulatory standing of kratom as a whole. Policymakers, researchers, and consumers must recognize the critical distinctions between traditional mitragyna speciosa products and these potent formulations. It is imperative to implement clear labeling, responsible marketing practices, and rigorous scientific research to ensure consumer safety and protect the reputation of natural kratom.
In conclusion, the emergence of 7-hydroxymitragynine products represents a significant departure from the traditional use of plain-leaf mitragyna speciosa, introducing heightened risks for consumers and the broader kratom community. These products, often marketed under the guise of natural kratom, carry uncharted safety concerns due to their alkaloid manipulation and lack of long-term studies.





Thank you for making such an informative blog post about these new, much stronger synthetic. The way its packaged and marketed by those that sell it leaves a bad taste in my mouth. I’ll stick with the tested products that I know what they are.